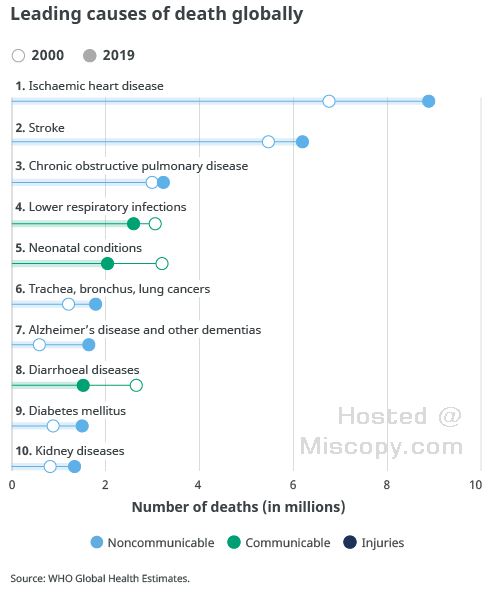
The World Health Organization (WHO) regularly publishes fact sheets on global health issues, including the top 10 causes of death worldwide. The following article provides an overview of the top 10 causes of death based on WHO data and highlights key information about each cause.
Introduction
The top 10 causes of death in the world account for more than 50% of all deaths. These causes are largely preventable and treatable, and addressing them is a major public health priority.
Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes, are the leading cause of death globally, accounting for 31% of all deaths. The risk factors for cardiovascular diseases include smoking, unhealthy diets, physical inactivity, and high blood pressure. Preventative measures include healthy lifestyle choices, regular exercise, and medication.
Cancer
Cancer is the second leading cause of death worldwide, responsible for 17% of all deaths. It is caused by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells, and risk factors include tobacco use, unhealthy diets, and exposure to radiation. Prevention and early detection are key to reducing the impact of cancer.
Respiratory Diseases
Respiratory diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and pneumonia, are the third leading cause of death, responsible for 10% of all deaths worldwide. Risk factors include smoking, air pollution, and exposure to respiratory infections. Prevention includes avoiding smoking and other respiratory irritants, as well as vaccination against respiratory infections.
Lower Respiratory Infections
Lower respiratory infections, such as pneumonia, are the fourth leading cause of death, responsible for 7% of all deaths worldwide. Risk factors include exposure to respiratory infections, weakened immune systems, and poor hygiene. Prevention includes vaccination, good hygiene practices, and avoiding exposure to infected individuals.
Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia
Alzheimer’s disease and dementia are the fifth leading cause of death worldwide, responsible for 5% of all deaths. These conditions are characterized by a decline in cognitive functioning and memory loss, and risk factors include age, genetics, and lifestyle factors such as poor diet and lack of exercise. Prevention and early diagnosis are key to managing these conditions.
Digestive Diseases
Digestive diseases, such as liver disease and cirrhosis, are the sixth leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for 3% of all deaths. Risk factors include excessive alcohol consumption, viral hepatitis, and unhealthy diets. Prevention includes vaccination against hepatitis, limiting alcohol intake, and maintaining a healthy diet.
Neonatal Disorders
Neonatal disorders, such as preterm birth complications and birth asphyxia, are the seventh leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for 2% of all deaths. Risk factors include poor maternal health, inadequate nutrition, and lack of access to healthcare. Prevention includes access to quality maternal and neonatal healthcare services.
Kidney Disease
Kidney disease is the eighth leading cause of death, responsible for 2% of all deaths worldwide. Risk factors include diabetes, high blood pressure, and other chronic diseases. Prevention includes managing these conditions and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Suicide
Suicide is the tenth leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for 1.4% of all deaths. Risk factors include mental illness, substance abuse, and social isolation. Prevention includes access to mental health services, social support networks, and awareness campaigns to reduce stigma surrounding mental illness.
Conclusion:
While there are many factors that can contribute to these top 10 causes of death, many of them are preventable through lifestyle changes and public health interventions. By reducing risk factors such as smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise, individuals can reduce their risk of developing many of these conditions.
Additionally, public health interventions such as vaccination campaigns and improvements in sanitation and hygiene can help to reduce the incidence of infectious diseases. It is important to continue to prioritize efforts to reduce the incidence of these top 10 causes of death, in order to improve global health outcomes and reduce premature mortality.
Sources:
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death
https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/leading-causes-of-death.htm